The Dynamic Resolution Manager, or DRM for short, is simple Windows program that resides in your tray. When right-clicked, it opens a menu, where you can choose a new resolution:
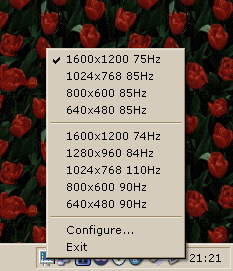
(Don't worry about the font in the screenshot -- it follows your system font. It's just that I personally happen to use Verdana as my system font.)
The "dynamic" part -- and the main selling point -- is that the program retains the window layout across resolutions. For example, let's say you have two windows side by side, together covering the entirety of the screen. When you switch to a lower resolution using drm, the windows will automatically be repositioned and resized to cover the exact same area; the full-screen side-by-side layout will be retained regardless of resolution. In other words, drm retains the centimeter-measured positions and sizes of all windows, rather than the pixel-measured.
The resizing and repositioning is instantaneous
and invisible, and it applies to all windows, even those that are
currently minimized. Below is an example, where the window layout is
retained when switching from 800x600 to 640x480.
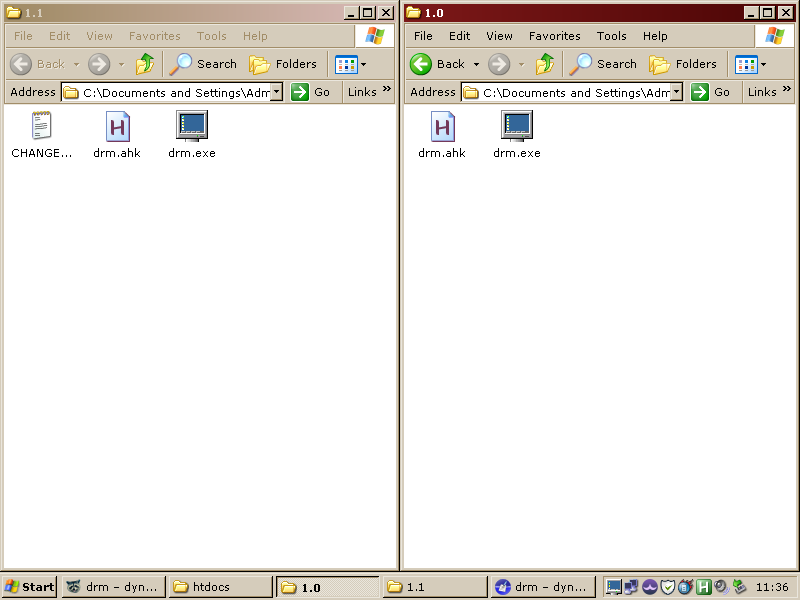
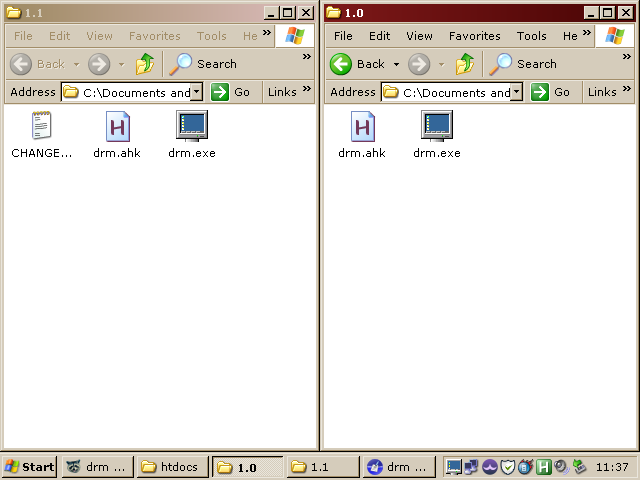
drm is configured via a set of registry keys located in
HKCU\Software\JohnAJ\DRM. They will be created automatically when
the program is launched for the first time.
| Key |
Description |
Example |
| Resolutions |
Set of custom resolutions. Since 1.4, refresh
rates can optionally be specified.* |
1600x1200 75Hz|1024x768 |
| Ignore |
Set of programs whose window position and size
should be ignored (1.2).** |
explorer.exe|2kclient.exe |
| IgnoreSize |
Set of programs whose window size should be
ignored, but window position retained (1.2). |
mpc-hc.exe|winamp.exe |
* Resolutions are specified using the following notation: width
"x" height [" " refresh rate "Hz"], with the section enclosed in
brackets being optional. Each resolution is then separated by a pipe (|)
character. Since 1.4.1, two pipe characters in a row (||) are
rendered as a separator in the menu.
** These windows will still be repositioned and resized, but always to
their original pixel-measured position and size. (As such, it will
still behave differently from Windows' normal operation, which is to
shrink windows that don't fit on screen.)
To quickly open the configuration in Registry Editor, click the Configure...
menu option. Note that you must restart drm in order for any
configuration changes to be applied.
If you want to customize the handling of specific windows further,
use the non-compiled version of drm, drm.ahk, which you can
easily modify yourself. Note that this
requires AutoHotKey to be
installed on your system.
Since version 1.3.2, drm.ahk includes a designated place
(around line 196, as of 1.4.2) where you can write your own custom
rules. The included example, shown below, would instruct drm to ignore
the size, but retain the position, of any window of the mpc-hc.exe
process with a client width of 294 pixels:
; Custom rules
; Example:
; if (exe = "mpc-hc.exe" and cw = 294)
; DoIgnoreSize := true
Code in this section of the program is run once for every window, whenever drm initiates a resolution change. You can easily control how drm should handle a specific window by setting one of the variables DoIgnore and DoIgnoreSize to true. This is equivalent to adding the program to the Ignore or IgnoreSize registry key.
This approach, while more powerful than the registry-based
configuration, requires some knowledge of AutoHotKey, some
understanding of drm's source code (which, however, is relatively
simple) and, finally, a slightly more manual update process, should a
new version of drm be released.
If you have any other issues or feature requests, feel free to contact me or
to modify the source
code yourself. If you add a feature or fix a bug yourself, please share
it!